

近日,國際著名學術期刊Journal of the American Chemical Society(IF 14.695)在線發表了中國藥科大學生命科學與技術學院徐寒梅教授團隊的最新研究成果“Micropeptide MIAC Inhibits HNSCC Progression by Interacting with Aquaporin 2”。課題組成員博士后李夢瑋和碩士生李鑫為論文的共同第一作者,徐寒梅教授為通訊作者,中國藥科大學為第一作者單位和第一通訊單位。江蘇省口腔醫院武和明主任和丁旭醫生對本論文亦有重要貢獻。
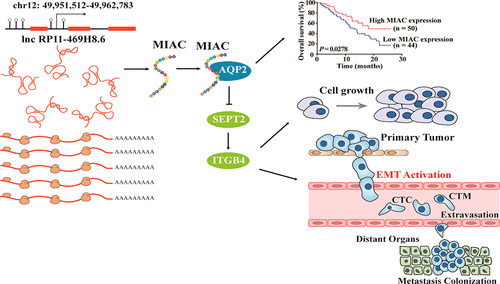
近年科學家研究發現長鏈非編碼RNA (long non coding RNA, lncRNAs,lncRNA)實際包含能編碼微肽 (micropeptides)的小開放閱讀框 (sORF),這為蛋白質組學研究提供了一個新的視角。目前已發現的由lncRNA編碼的微肽報道并不多。本研究首次在頭頸鱗癌中發現由lncRNA AC025154.2編碼的全新內源性微肽MIAC,體內外實驗發現MIAC能抑制頭頸鱗癌的增殖和轉移,蛋白質譜和酵母雙雜交結果顯示MIAC能結合水通道蛋白,通過調控Sept2/ITGB4表達抑制骨架蛋白重排,最終抑制頭頸鱗癌進展。結合500例TCGA數據庫頭頸鱗癌RNA-seq數據和154例臨床樣本檢測分析證實MIAC在頭頸鱗癌組織中表達顯著低于癌旁組織,其表達水平與患者總生存率呈正相關,與臨床病理分期,區域淋巴結轉移呈負相關,提示MIAC可以作為頭頸鱗癌臨床診斷和預后的潛在標志物。
同時,課題組成員博士后王穎和碩士生陸繼強為共同第一作者,徐寒梅教授為通訊作者在Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids(IF 5.919)雜志上發表了小RNA分子的最新研究。研究圍繞著食管癌細胞來源的外泌體miR-181b-5p展開,解析了其調控腫瘤血管生成的分子機制,有望為食管癌患者的臨床診治和預后評估提供新型的生物標記分子和潛在的藥物靶點。
此外,近三年徐寒梅教授團隊在RNA與腫瘤關系的其它研究成果還發表于Clin Cancer Res (Lin C, Zhang S, Xu H*.2018 Jan 15;24(2):486-498, IF 8.911),Oncogene (Lin C, Wang Y, Xu H*. 2017 Sep 21;36(38):5392-5406, IF 6.854),Cell Death Dis (Li M, Han Y, Xu H*. 2018 Jan 24;9(2):91, IF 5.959)等雜志上。
Abstract
Several important micropeptides encoded by noncoding RNAs have been identified in recent years; however, there have never been any reports of micropeptides in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Here we report the discovery and characterization of a human endogenous peptide named micropeptide inhibiting actin cytoskeleton (MIAC). Comprehensive analysis of the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) database (n = 500), clinical fresh samples (n = 94), and tissue microarrays (n = 60) revealed that lower MIAC expression is correlated with poor overall survival of HNSCC patients. Meanwhile, RNA-sequencing analysis of 9657 human tissues across 32 cancer types from TCGA cohorts found that MIAC is significantly associated with the progression of 5 other different tumors. Mechanistically, MIAC directly interacts with AQP2 (Aquaporin 2) to inhibit the actin cytoskeleton by regulating SEPT2 (Septin 2)/ITGB4 (Integrin Beta 4) and ultimately suppressing the tumor growth and metastasis of HNSCC. Collectively, the mechanism investigation and evaluation of MIAC activity in vivo and in vitro highlights that MIAC plays an important role in HNSCC tumorigenesis.
聲明:化學加刊發或者轉載此文只是出于傳遞、分享更多信息之目的,并不意味認同其觀點或證實其描述。若有來源標注錯誤或侵犯了您的合法權益,請作者持權屬證明與本網聯系,我們將及時更正、刪除,謝謝。 電話:18676881059,郵箱:gongjian@huaxuejia.cn